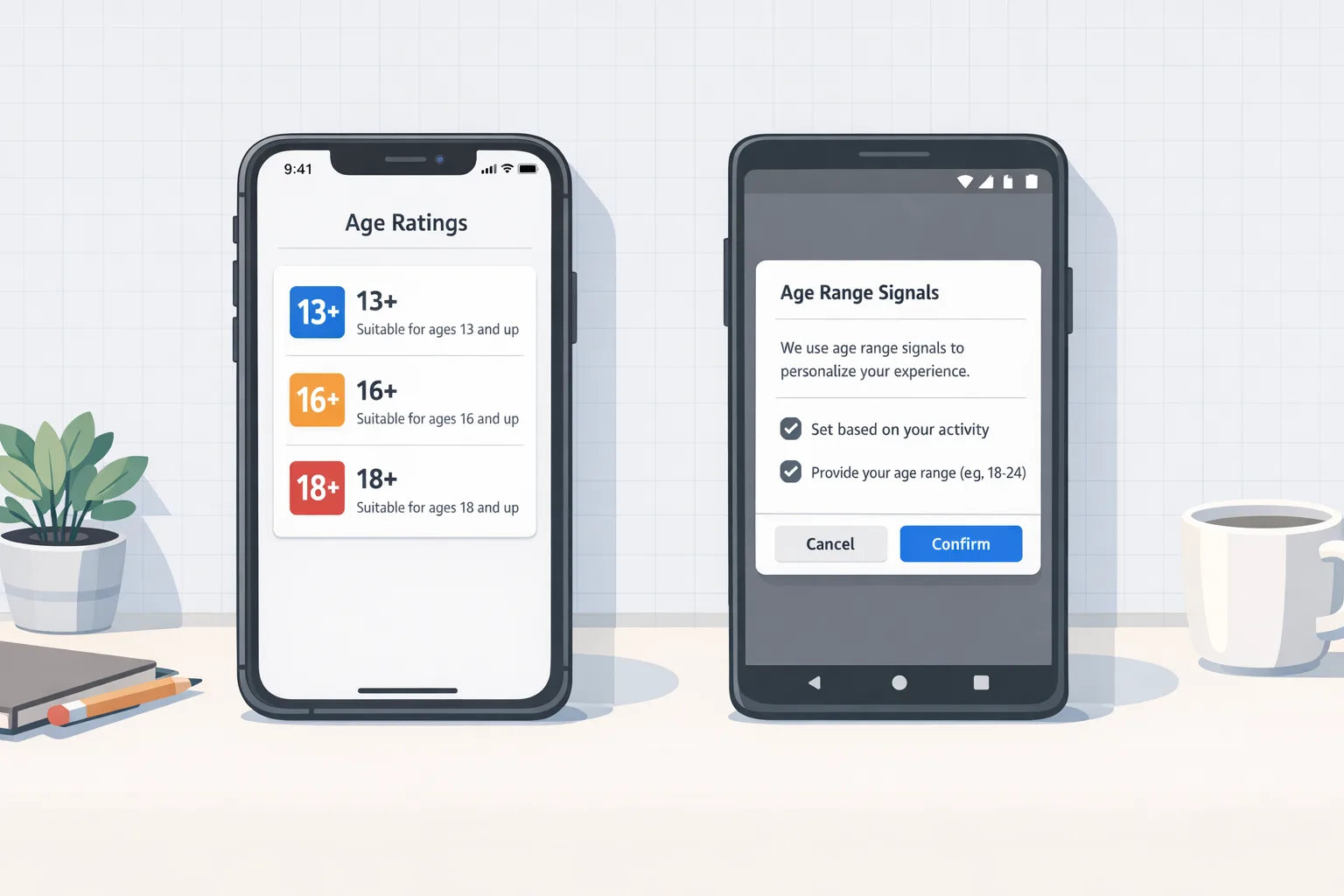
App Store Age Ratings: The 30‑Day Compliance Plan
Apple’s more granular App Store age ratings and the new Declared Age Range API have moved from “coming soon” to “ship now” territory. Over the past year Apple introduced teen‑specific tiers (13+, 16+, 18+), updated App Store pages to disclose sensitive capabilities like UGC and messaging, and rolled out a privacy‑preserving way to request a user’s age range at runtime. Meanwhile, state bills are pressuring marketplaces to enforce age assurance. If you own a consumer app today, you need a plan that delivers compliance without wrecking activation or LTV.

What actually changed—and when
Let’s anchor the timeline so your roadmap isn’t guessing. In June 2025, Apple announced expanded parental protections and said App Store ratings would split the teen band into 13+, 16+, and 18+. By mid‑2025, Apple briefed developers to re‑answer the age‑rating questionnaire and disclose capabilities like user‑generated content, messaging, ads, and built‑in parental controls. In fall 2025, Apple outlined region‑specific compliance plans (for example, state laws that contemplated app‑store‑level age checks). On December 23, 2025, a federal court blocked Texas’s SB 2420 ahead of its January 1, 2026 effective date, but Apple’s privacy‑centric approach—device‑level age ranges, family controls, and runtime APIs—kept moving forward. As of February 2026, you should treat the rating overhaul and the API as live‑fire requirements, with state‑level mandates still evolving.
Translation: even with legal turbulence, the direction is clear. Apple wants developers to implement age‑appropriate experiences that lean on system signals and explicit parental governance—not DIY data collection. Teams that adopt this posture now reduce review friction and avoid expensive reworks later.
Primary concept: how the Declared Age Range API fits
The API gives you a structured, OS‑mediated way to ask for a person’s age range (not their birthday). Apple’s UI mediates consent; you receive a lower bound and metadata indicating whether the range was declared by the user or set through parental controls. You can pass in up to three “gates” (for example 13, 16, 18) and get back a response you can map to content, features, and nudges.
A few practical realities from shipping this in production:
- Availability varies with account setup, family sharing, and region. Handle “not available” gracefully and fall back to a conservative default for risky features (for example, public posting).
- The OS may override your gating in some geos. Don’t hard‑code expectations—treat the API as authoritative when it returns data, but design for nulls.
- Consent can change. A teen’s age bracket advances; parents may revoke sharing. Cache minimally and re‑check at natural boundaries (login, profile flows, sensitive actions).
Why this matters for product metrics
Age gating can hurt activation if you bolt it on carelessly. Done well, it protects minors, reduces review escalations, and can even improve trust with adults. We’ve seen live apps maintain 95–98% day‑one conversion by deferring any gating until the first sensitive action (posting, joining a live chat, or enabling DMs) rather than blocking the entire first‑run.
Use App Store age ratings to drive scope, not guesswork
The new teen tiers aren’t cosmetic. Tie your behaviors to the ratings you declare:
- 13+ apps: default to private profiles for teens, limit outbound links, and suppress public discovery until an adult confirms.
- 16+ apps: enable most community features but keep DM and joining groups behind an age gate with safety prompts.
- 18+ apps: implement a clear on‑ramp for identity/age checks if content warrants it, plus granular content filters for adults who want them.
Here’s the thing—Apple’s review now looks for alignment between the rating you pick, the disclosures on your App Store page, and actual runtime behavior. If you claim “parental controls available,” they need to be discoverable, functional, and enforced.
The 30‑day compliance plan (do this now)
Ship in one sprint? Possible. Two sprints? Comfortable. Here’s a realistic 30‑day plan we’ve used with consumer clients.
Week 1: classify risk and decide gates
- Map sensitive surfaces: messaging, UGC submission, livestreaming, voice/video chat, payments, external links, location sharing, and ads personalization.
- Pick your gates: most apps can set 13/16/18; some 13/18 is enough. Document which features require which minimum.
- Align with disclosure: update the App Store questionnaire answers to match reality. If you say you moderate UGC, describe how in Review Notes and your Safety section.
Week 2: wire the API and fallbacks
- Runtime request: call the Declared Age Range API the first time a user attempts a gated action. If unavailable, ask the user to proceed in a “safe default” mode (for example, read‑only), and expose a one‑tap “Verify age to unlock” button.
- Cache lightly: memoize the latest result with a timestamp; re‑verify at login and before enabling new sensitive features. Never store DOB; don’t export age to analytics vendors.
- Kill switches: add remote config to disable specific features by segment and region in case a state mandate changes mid‑sprint.
Week 3: ship the UX the review team expects
- Clear prompts: “We’ll ask iOS to share your age range so we can enable DMs safely.” Link to a privacy page detailing your logic.
- Visible controls: a dedicated Safety & Privacy screen with toggles for discoverability, DMs, and content filters. Teens should see stricter defaults.
- On‑fail paths: if age sharing is declined, offer limited mode and explain benefits—don’t brick the session.
Week 4: verify, document, submit
- Test matrix: adult account, teen account with parental controls, no age data; cover upgrade and logout/login cycles.
- Review notes: add a short explainer—where you call the API, what features are gated, and how parental controls interact.
- Release discipline: keep the feature behind a feature flag for 48 hours; monitor crash‑free sessions and conversion to first gated action.
If you need a deeper checklist for your team, see our shipping guide on age‑aware release checklists and our practical build‑age‑aware patterns.
People also ask: quick answers for your PM and legal teams
Do we still need to act if the Texas law was blocked?
Yes. The court’s December 23, 2025 injunction paused one state law; it didn’t roll back Apple’s rating overhaul or the runtime API. Apple’s product and doc changes are platform‑level and continue to influence review. Treat state actions as additional constraints, not the driver of your plan.
Where should we ask for age—on sign‑up or later?
Gate at the first sensitive action, not at account creation. That keeps your activation flow clean for adults while maintaining safety when it matters. If you collect age ranges too early, you’ll pay in conversion for use cases that never touch risky features.
Can we store the result in our backend?
Store only the minimum needed. A boolean flag like “eligibleForDMs” with a timestamp is usually enough. Recompute when the system shares a new range or when a parent updates controls. Avoid sending age data to third‑party SDKs or analytics.
What about Google Play?
Play has mature Families policies and age‑appropriate design guidance. If you’re multi‑platform, design once for the strictest bar. We’ve had success mirroring the same feature gates on Android using first‑run questions, supervised account signals, and parental approvals without collecting DOB.
Design patterns that pass review
You don’t need a wall of modals. Use progressive disclosure:
- Deferred gating: let users browse, then request age range when they attempt to post or open DMs.
- Contextual safety nudges: before enabling DMs, show a short explainer and a default of “Friends only” for teens.
- Transparent controls: a Safety screen accessible from Profile, with copy tailored by age range.
- Parent‑visible states: reflect whether a parent set the age range (the API exposes declaration type) and disable sensitive toggles accordingly.
For a deeper UX walkthrough, our article on shipping a compliant UX fast covers patterns and microcopy that reduce friction.
Engineering details that matter
Here’s a pragmatic approach to the API and edge cases:
- Gates: pass the exact thresholds you enforce (for example, 13, 16, 18). Keep them in config so policy updates don’t require a client release.
- Null‑safe logic: if the response is “not available,” default to safest behavior for features that could connect a teen to strangers (public comments, open DMs) and let the rest of the app work.
- Re‑request rules: only re‑prompt after a material feature attempt or when the user navigates to Safety & Privacy. Avoid nag loops.
- Telemetry: instrument count of prompts, accepts, declines, and feature unlock rates by platform and country. These become your KPIs.
- Testing: mock API responses to simulate child, teen, adult, and unavailable states; run them through CI to prevent regressions.
Privacy and data sharing: the non‑negotiables
Two clear signals from Apple’s policy direction: keep age data local and don’t leak it to third parties. If you use generative AI features, treat any age‑related signals as sensitive. Keep prompts and responses on‑device where possible; if you must call external services, don’t pass age or parental status, and redact PII. Document this in your privacy policy and Review Notes.
Also, ensure your ad tech setup respects teen profiles. That may mean disabling personalized ads for under‑18 ranges and adopting contextual targeting only. Document which SDKs are active for minors and verify they’re configured to a teen‑safe mode.
App Store age ratings: set them with intent
Your App Store age ratings should be a direct outcome of your feature gates and moderation posture. If you’re 13+, your defaults must reflect it: slower discovery, stricter DM rules, and robust in‑app reporting. If you’re 16+, you can open more, but keep guardian‑friendly explanations and visible safety switches. If you’re 18+, make consent clear, provide filters, and consider additional checks for particularly sensitive content categories.
Compliance isn’t just iOS: align policy, ops, and support
Product compliance fails when policy and operations lag. Publish a short, plain‑language Safety page that explains your gating logic and reporting tools. Train moderation on how teen defaults differ. Update support macros to answer “Why can’t I DM?” with the right steps and a link to parental consent and Safety settings.
Metrics that prove it’s working
Track four numbers weekly post‑launch:
- Prompt acceptance rate (target: >80% for adults at first sensitive action).
- Feature unlock conversion (adults and teens separately).
- Safety incident rate per 1,000 active users (should decline as gates roll out).
- App Review rejections related to age or safety (trend toward zero by the second update).
If acceptance dips, move the prompt later or tighten the copy. If incidents rise, reconsider which features demand 16+ or 18+.
Common pitfalls (and how to avoid them)
- Blanket hard blocks: turning the whole app off for teens drives churn. Gate surgically.
- Storing DOBs: unnecessary and risky. Use the range only.
- Leaky analytics: sending age flags to third‑party SDKs can trigger review issues. Keep it first‑party.
- One‑time checks: teens age into new brackets; plan for it. Re‑evaluate on login and before enabling new features.
- Mismatch with listing: if your App Store page claims “parental controls,” reviewers will test them.
Security footnote: ship like you mean it
Treat this as a security‑adjacent feature set. Use feature flags, progressive rollouts, and a hotfix plan. If your Node.js backend powers consent flows or moderation, keep a release checklist handy—our security release playbook is a good template to avoid regressions when policy toggles change at 5 p.m. on a Friday.
What to do next (the one‑pager)
- Pick gates (13/16/18) and map each sensitive feature to a minimum age.
- Implement the runtime request at first sensitive action; add safe fallbacks.
- Publish a Safety page and update App Store disclosures to match behavior.
- Instrument prompts, accepts, declines, and unlocks; review weekly.
- Add region flags so you can adapt quickly if a state mandate lands.
If you want an expert pair of hands, our team does end‑to‑end app audits, API integration, and UX tuning. See our mobile services and what we do, or reach out via contact.




Comments
Be the first to comment.