App Store Age Rating 2026: What to Fix This Week
Apple’s updated framework for App Store age rating 2026 is now active, and teams that ignored the questionnaire update are already seeing friction in submission. At the same time, Google Play’s Age Signals is maturing with clearer documentation on supervised users, approval flows, and default age ranges. Add governments floating under‑16 social bans and app‑store age verification mandates, and you’ve got urgency with real product implications. Here’s the plan to fix what matters this week—and to set up an age‑aware foundation you won’t have to rebuild in six months.

What changed on Apple—and why your submission may stall
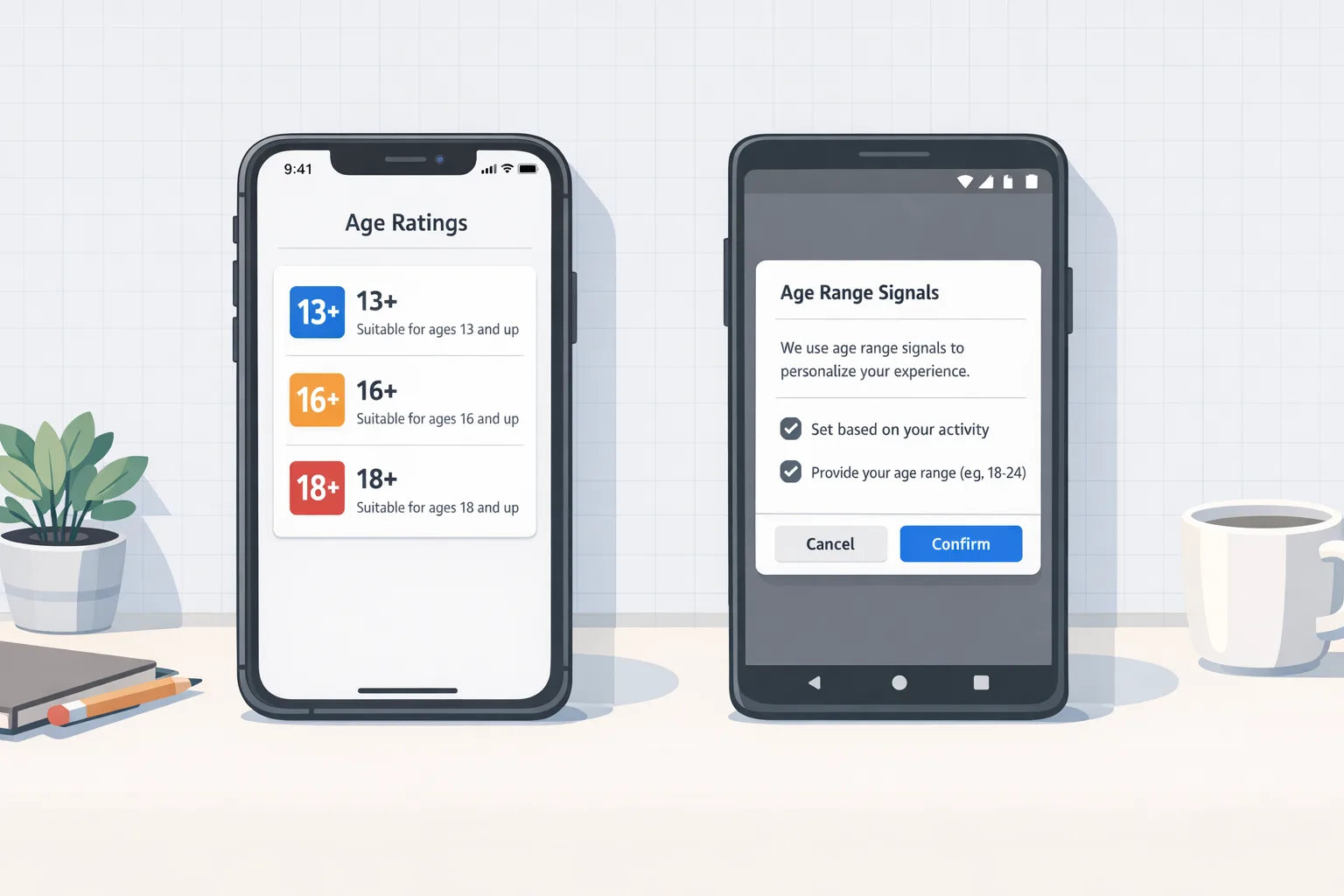
On January 31, 2026, Apple finalized an age-rating update: ratings for all apps were aligned to the new system, and developers were instructed to answer updated questions in App Store Connect to avoid submission interruptions. The change also notes the minimum OS families (iOS 26, iPadOS 26, macOS Tahoe 26, tvOS 26, visionOS 26, watchOS 26) where the new ratings are reflected on-device. If you missed the updated questionnaire, your release train can slip for avoidable reasons. (developer.apple.com)
Here’s the thing: Apple doesn’t give you an API for a user’s age or a dynamic “age signal.” Your responsibility is to classify content accurately, expose age-appropriate UX, and ensure features that require maturity—public profiles, open DMs, peer-to-peer payments, explicit content access—are responsibly gated. Treat age rating as your baseline contract with Apple’s review process and users, not the end of the conversation.
Google Play Age Signals: what it actually returns (and what it doesn’t)
Google’s Play Age Signals provides a structured way to adapt your app based on a user’s status: VERIFIED (18+), SUPERVISED (parent-managed), SUPERVISED_APPROVAL_PENDING, SUPERVISED_APPROVAL_DENIED, UNKNOWN, or null for non-applicable cases. The API covers default age bands (0–12, 13–15, 16–17, 18+) and supports custom bands defined in Play Console. Documentation as of January 30, 2026, clarifies the responses, the role of mostRecentApprovalDate, and the fact that it’s supported from Android 6.0+. It’s still on developers to enforce an age-appropriate experience. (developer.android.com)
There’s also a “significant change” workflow. You can announce upcoming changes (for example, enabling UGC replies for 13–15) with an effective date. Play then triggers parental approval requests in jurisdictions that require it and updates API status until a parent approves or denies. This turns risky “ship and hope” moments into explicit, auditable consent events. (developer.android.com)
The regulatory drumbeat you can’t ignore
In the last few days, Spain signaled intent to ban social media use under age 16, with real age verification and executive accountability on the table. Whether or not this proposal clears parliament, the direction of travel is obvious: age checks must be effective, not perfunctory. France and Australia are moving in similar directions. Expect more regions to copy the strongest provisions. (ft.com)
Closer to home for U.S. developers, an Alabama bill advanced that would shift age verification and parental consent responsibilities to app stores, with real-time age and consent data available to developers. Supporters argue it improves safety; developer groups warn it could mandate over-collection and impose heavy burdens on small teams. If it passes, expect other states to draft me‑too legislation. Design your stack to adapt by policy toggle, not hardcoded assumptions. (axios.com)
Primary keyword question: What does “App Store age rating 2026” require of my product team?
Short answer: classify accurately and build an age-aware UX. The rating gates distribution and discoverability; your app still needs in‑app controls for riskier features, privacy defaults tuned for teens, and parental involvement where applicable. Your engineering, product, design, and policy folks need a shared checklist—and a way to test it.
Let’s get practical: the ADVANCE model for age-aware UX
Use this seven‑step framework across iOS and Android. Think of it as a release‑quality spec you can hand to engineering today—and keep evolving as new laws and store guidance arrives.
A — Assess content and features
Inventory everything users can see or do: feeds, profiles, UGC attachments, private messaging, livestreaming, tipping, third‑party links, and external browsers. Map each feature to a minimum age tier, starting with conservative defaults. On iOS, ensure your App Store questionnaire reflects this map so your classification, screenshots, and UX tell a coherent story to reviewers. (developer.apple.com)
D — Detect the user’s context
On Android, call Play Age Signals early after launch and on key state changes (login, profile completion). Treat responses as hints with guardrails: VERIFIED may unlock adult experiences; SUPERVISED gets reduced reach and stronger defaults; UNKNOWN must fall back to conservative modes. Cache carefully and revalidate on app open to stay current with parental approvals. (developer.android.com)
V — Verify when it’s high risk
For account recovery via SMS, peer‑to‑peer commerce, or public content visibility, consider an in‑app age‑check pathway. You can use third‑party KYC vendors where legitimate interests justify it, but minimize data retention and give a no‑ID off‑ramp (for example, “stay in limited mode”). Avoid blanket checks that degrade UX for adults; use verification only where risk justifies friction.
A — Adapt features and defaults
Design feature flags around age tiers: auto‑private profiles for teens, limited public reply exposure, no location sharing, no open DMs from unknowns, and safe search defaults. If your app includes payments, require an extra confirmation for supervised users. For UGC, restrict link posting and media types by age. Make these flags server‑driven so you can respond to new laws without a client release.
N — Notify and capture parental approvals (Android)
Use the Play Console’s “Significant changes” flow for teen-impacting features and track mostRecentApprovalDate. In regions where Play triggers parental flows, your app can gracefully throttle features until approval arrives; your analytics should record state transitions to prove you did the right thing. (developer.android.com)
C — Capture consent and explain tradeoffs
Plain‑English disclosures beat legalese. Explain what changes for younger users and why. Offer a clear settings page that summarizes restrictions and links to your privacy notice. Teens should understand what’s on and what’s deliberately off; parents should see that you respect autonomy while reducing risk.
E — Evaluate and audit
Continuously test edge cases: logged‑out flows, device family controls, VPNs and region changes, and reinstalls. Log state decisions (“why was this feature gated?”) so you can audit moderation outcomes. Build dashboards that track approvals, denials, UNKNOWN rates, and feature unlocks by cohort.
People also ask: Do I need age verification if my app isn’t “for kids”?
Probably yes—if it offers high‑risk features that change meaningfully for minors. You don’t need to re‑invent KYC for every click, but you do need tiered defaults. The legal threshold varies by region; the product threshold is simpler: if misuse by a teen could lead to harm, dial down the feature by default and provide a path to supervised or verified use.
People also ask: How do Play Age Signals and Apple’s rating relate?
Think of Apple’s rating as your public label and front‑door policy, enforced by review and platform controls. Play Age Signals is an in‑app signal to adapt behavior at runtime. They’re complementary: one governs distribution and expectation‑setting; the other informs dynamic UX tuning. Both expect you to implement the actual guardrails. (developer.apple.com)
A 10‑point shipping checklist for the next two sprints
Use this when triaging across iOS and Android. Treat each item as shippable in isolation; you don’t need to boil the ocean to get safer fast.
- Confirm your current Apple rating and re‑answer the new questions in App Store Connect; add reviewer notes that explain your age‑tier decisions.
- Map features to age tiers and create server‑side flags to toggle riskier capabilities by tier.
- Integrate Play Age Signals on Android and record state transitions for analytics and audits. Gracefully handle null/UNKNOWN.
- Define “significant changes,” schedule them in Play Console, and wire a UI to reflect pending parental approvals. (developer.android.com)
- Ship teen‑safe defaults: auto‑private profiles, stricter DM rules, and link‑posting limits for supervised users.
- Instrument a “Why is this restricted?” explainer panel that clarifies limits and offers a safe pathway to unlocks where allowed.
- Review payments: disable peer‑to‑peer for minors; require stronger confirmation for supervised users.
- Update moderation: pre‑moderate media uploads for supervised accounts; rate‑limit at-risk interactions.
- Run adversarial tests: region changes, reinstall, offline mode, cached signals, parental approval flips mid‑session.
- Align your privacy and support docs; make sure customer support has a playbook for “My teen can’t do X—why?”
Risks, limits, and edge cases to plan for
Signals aren’t perfect. Android’s API may return UNKNOWN; some regions won’t participate in parental approval flows; supervised accounts can migrate across devices; and network dropouts can freeze a user in the wrong tier. Design idempotent checks and retry logic. On iOS, without an age API, you’ll rely on a combination of platform‑level family controls and in‑app logic—so keep your enforcement server‑driven and transparent to users. (developer.android.com)
Policy churn is real. Spain’s proposal highlights how quickly rules can change; U.S. states may diverge dramatically. Treat region as a first‑class dimension in your authorization model, not a decoration on the UI. That way, when a jurisdiction flips from “guidance” to “mandate,” you don’t need a rewrite—just a config change and QA cycle. (ft.com)
Data you should track from day one
Track a few metrics relentlessly: percentage of users by age tier; supervised vs. verified; parental approval latency; feature unlock rates; and abuse flags per tier. On Android, tie mostRecentApprovalDate to capability unlocks and report on the delta between “approval pending” and “approval granted.” On iOS, track user‑facing opt‑ins for riskier features as a proxy for maturity. These numbers help you defend decisions to stores and regulators—and improve UX over time. (developer.android.com)
Realistic implementation timeline (starting this week)
This is the minimum viable path I’ve used with teams shipping social, media, and marketplace apps:
- Week 1: Rate audit and feature‑to‑tier map; App Store questionnaire updated; Android API scoping; server feature flags scaffolded. (developer.apple.com)
- Weeks 2–3: Android integration + analytics events; iOS server‑driven gating; teen‑safe defaults shipped behind flags; moderation rules split by tier.
- Week 4: Significant change scheduling in Play Console; parental approval UX states; support docs and FAQ updates. (developer.android.com)
- Ongoing: Region toggles, A/B tests for friction, regulator watchlist, and quarterly audits.
Where teams get stuck (and how to avoid it)
Two patterns slow teams down. First, mixing policy and product: a “legal says no” culture that hides requirements inside dense docs instead of user stories. Translate every rule into an observable behavior or state change; ship it like a feature. Second, hardcoding age logic in clients. You need server‑driven enforcement so you can pivot quickly when a policy, OS, or store rule changes.
What to do next
Want a deeper handoff-ready blueprint? Start with our practical deep dives on age-aware design and shipping under tight deadlines. If you’re staring at a submission blocker or a risky feature launch, our team can help you get it out the door safely.
- Study a fast-track approach in Ship a compliant UX now.
- Build durable patterns with Build age‑aware apps.
- Cross‑platform planning? See our App Store vs. Play Age Signals guide.
- Need help from specialists? Explore mobile product services or talk to us.
Zooming out: why this matters for growth, not just compliance
Age-aware UX isn’t just guardrails—it’s product strategy. Safer defaults cut moderation costs, boost trust, and reduce churn from negative experiences. Clear parental approvals increase legitimacy for teen‑oriented features. And strong instrumentation means you can say “yes” to innovative features with confidence because you can dial them back by tier and region without a rewrite. Do it right and you’ll ship faster, pass review with fewer surprises, and build the kind of reputation stores reward.
Final word for busy teams
The platform winds have shifted. Apple’s rating update is live, Play’s signals are actionable, and lawmakers are moving from guidelines to mandates. Ship the ADVANCE model, keep your enforcement server‑driven, and make parental approvals observable. Nail this now and your product will feel safer, review will go smoother, and you’ll be ready when the next jurisdiction tightens the rules. If you need a partner, you know where to find us.




Comments
Be the first to comment.