Google Play External Links in the U.S.: 2026 Playbook
Google Play external links are finally arriving for U.S. apps—and the window to ship is tight. As of January 2026, Google’s programs for External Content Links and alternative billing are rolling out with a compliance deadline on January 28, 2026. There’s upside in owning your checkout and onboarding funnel, but there are also service fees, tracking requirements, and a few gotchas. This guide lays out what changed, how the proposed fees work, and a concrete engineering plan to implement the flow with Play Billing Library 8.2.1.
What changed in January 2026—and why it matters
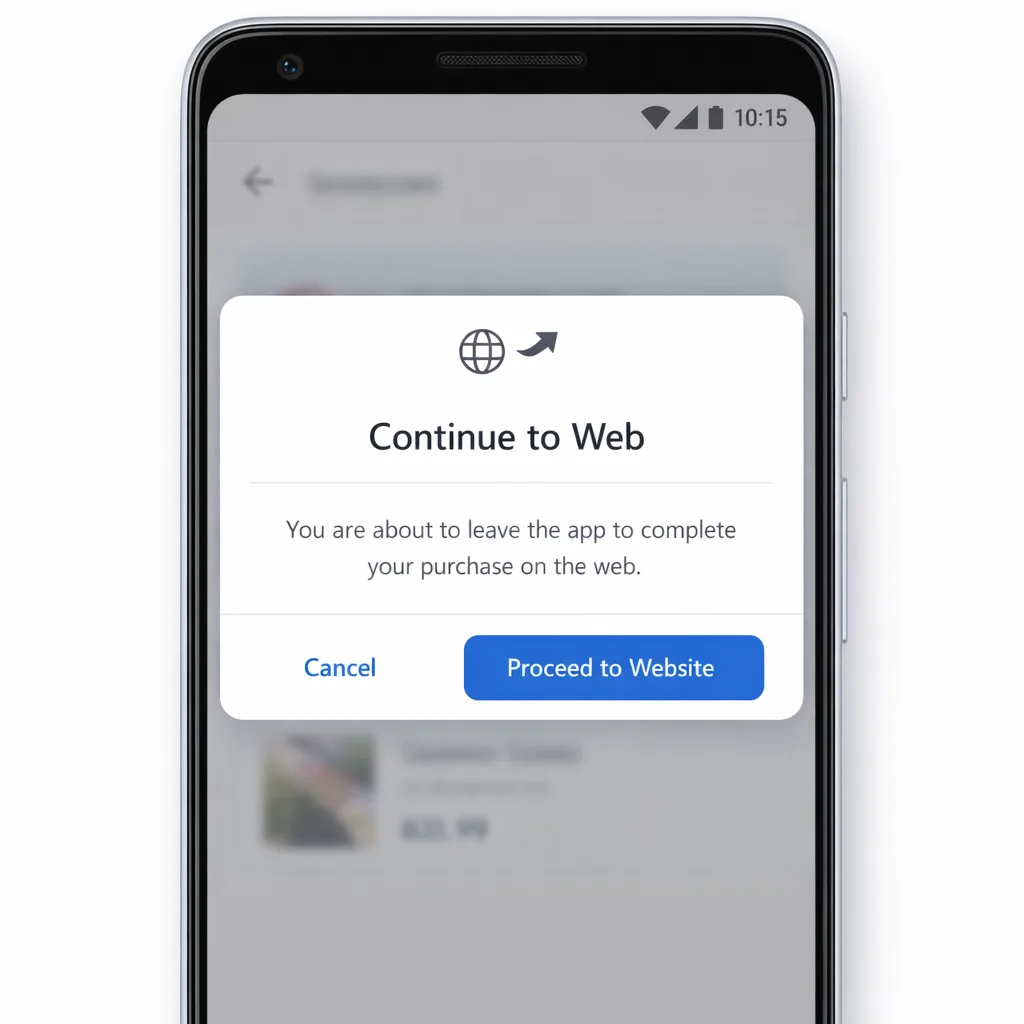
U.S. developers can now enroll in Google’s External Content Links program to do two things inside their Android apps: link users to purchase digital content on the web, and link them to download an app outside Google Play. For many teams, that reopens direct-to-consumer playbooks that were hard to justify under past policies.
Two dates to tattoo on your roadmap: January 28, 2026 is when apps linking out must be compliant with Google’s program requirements; and January 31, 2026 is when Apple’s App Store Connect age rating questionnaire updates become mandatory for iOS submissions. In other words, cross‑platform teams are juggling both changes in the same sprint. If you haven’t already briefed PMs, legal, and payments, now’s the moment.
Primary keyword: Google Play external links
You’ll see the term “Google Play external links” used interchangeably with “External Content Links.” In practice, the program covers off‑Play transactions and, if you choose, links to external app downloads. Enrollment and integration are required; this isn’t a free‑for‑all—Google expects specific UI, information screens, tokenized tracking for external purchases, and updated SDK versions.
A quick timeline developers can trust
Here’s the clean, ship‑ready timeline for your release managers and compliance leads:
• December 9, 2025: Google posts the U.S. policy announcement and opens programs for alternative billing and external content links.
• January 22, 2026: Court hearing scheduled related to the proposed settlement and remedies that could affect fee timing and structure.
• January 28, 2026: U.S. apps using external links or alternative billing must be enrolled and compliant.
• January 31, 2026: Apple requires developers to complete the updated App Store age rating questionnaire or updates will be blocked in App Store Connect.
Bookmark those dates and lock your internal approvals around them.
Should you adopt External Content Links?
Short answer: for many apps, yes—but only if you model costs precisely and sequence your rollout. The financial logic depends on three levers: service fees on off‑Play transactions, an initial acquisition component for users within six months of a Play install, and a potential fixed fee per install when your in‑app link leads to an external app download within a defined window. Google has indicated percentages for off‑Play transactions and, for external downloads, country‑ and category‑specific fixed fees. Reporting suggests U.S. rates under consideration of approximately $2.85 per app install and $3.65 per game install when completed within 24 hours of the click. Treat these figures as directional until Google publishes final U.S. rate cards, and watch the January 22 hearing because it can influence fees and timing.
How the fee stack typically works
Think in layers:
• Initial acquisition: 3% on qualifying transactions if they occur within six months of the user’s last Play‑managed install of your app or game. After six months, this component drops to 0%.
• Ongoing service: 10% on qualifying off‑Play transactions while your Play listing benefits from Play services (safety scanning, discovery, family controls, etc.).
• External download fee (only if you deep‑link to an external APK/app store install): a fixed amount per install, by country and app category, when completed shortly after the click. U.S. figures being floated are $2.85 for apps and $3.65 for games per install in that window.
If/when Google begins assessing the separate fee schedule for alternative payments or external link transactions, expect numbers like 20% on most one‑time digital purchases via external links and 10% on subscriptions. Layer your own payment processor rates on top (~2.9%–5%, depending on method and fraud tools). If the court shifts terms, revisit your model immediately.
Two realistic scenarios
Scenario A: a $50 non‑subscription purchase triggered from an in‑app link during the first six months after a Play install. Budget 3% initial acquisition + 10% ongoing service = 13% to Google on that off‑Play transaction, plus your processor fee. Net to you before processor: $43.50. If Google later activates the 20% external‑link transaction rate, your stack becomes 3% + 10% + 20% = 33% before processor—no longer attractive. That’s why many teams are prioritizing subscriptions first.
Scenario B: a $9.99 monthly subscription purchased via your web checkout. Model 10% as the ongoing service (and 0% initial acquisition once you’re past six months), plus your payment processor. If Google begins charging the 10% subscription rate on external link conversions, you’re still around 10%–15% total before processor—a workable margin for most apps with decent retention.
Engineering plan: ship External Content Links in 10 days
Here’s the implementation path we’ve used with product teams that needed to move fast without skipping compliance.
Day 1–2: Decide your flows and scope
• Choose which SKUs go off‑Play (start with subscriptions or high‑AOV items).
• Determine if you’ll link to external app installs at all. If yes, keep it to a separate SKU or experiment; the fixed per‑install fee can add up fast.
• Write the UX copy for the information screen: you must disclose you’re leaving the app to complete a purchase or install elsewhere, who’s charging, refund path, and customer support location.
• Map parity: if you offer Google Play Billing and an external option, surface both clearly without dark patterns.
Day 3–4: Upgrade and integrate
• Update to Play Billing Library 8.2.1 or higher—this is non‑negotiable for program eligibility.
• Implement the external transaction token flow. When the user completes a web purchase, call back to Play with the token to record a successful off‑Play transaction.
• If you’re experimenting with external installs, implement the link tracking parameters so Google can attribute installs that occur within the allowed window.
Day 5–6: Server, security, and reporting
• Harden your webhook endpoints for purchase confirmation and idempotency; log token mismatches explicitly.
• Implement receipt records that include source (Play listing vs. organic web), SKU, and attribution window. You’ll need this for audits and finance reconciliation.
• Wire up refunds and customer support flows: you, not Google, own the user relationship off‑Play.
Day 7: Play Console configuration
• Enroll in External Content Links; verify eligibility for your package names.
• Upload your information screen assets/copy and enable required toggles.
• Document what you’re linking to (web checkout URLs, install destinations) to keep legal and compliance in the loop.
Day 8–9: QA with edge cases
• Test on fresh Play installs and on devices older than six months to validate the acquisition window logic.
• Validate failure paths: user cancels on web checkout, token not returned, slow network, and expired token.
• Test family and parental controls; don’t accidentally bypass Play’s guardrails for restricted accounts.
Day 10: Launch with guardrails
• Roll out behind a server‑controlled feature flag at 5–10% of eligible traffic; measure conversion and support tickets.
• Monitor attribution accuracy for 24–48 hours; reconcile web orders vs. Play‑acknowledged tokens.
• Document your rollback plan in the runbook.
Gotchas most teams hit at least once
• Stale tokens: external transaction tokens aren’t reusable; expire them quickly and handle retries gracefully.
• Support drift: users will contact Google for refunds even when you own the payment. Put “Refunds managed by [Your Company]” in both the information screen and receipt emails.
• Analytics gaps: you’ll need a cross‑surface funnel view (App → Web → Purchase) with identical SKU ids. If you can’t stitch, you can’t optimize.
People also ask: key questions answered
Can games use external links in the U.S.?
Yes, games can participate, but the external install fee being discussed is higher for games than apps. If you operate at large scale, even a small take‑rate delta multiplied by volume will dwarf your checkout processing fees. Model carefully before linking players to a separate APK or store.
Is alternative billing better than external links?
Different tradeoffs. Alternative billing keeps the user in‑app but still reports to Google and, historically, has carried a smaller discount from Google’s standard service fee. External links give you more control over the checkout UX and promotions, but you add information screens, a token handshake, and potentially a per‑install fee if you push an external app download.
Will Google charge fees on off‑Play purchases and installs?
Google has outlined service fees for off‑Play transactions and fixed fees for installs following in‑app links to external app downloads. Some of these fees have been described as intended or forthcoming in the U.S., pending legal and program updates. Build the integration now to meet the January 28 deadline and keep your models flexible while final U.S. rate cards and timing settle.
How this intersects with iOS in January
While Android engineers sprint on external links, your iOS team must finish Apple’s updated age rating questionnaire in App Store Connect by January 31, 2026. Ratings were auto‑mapped to the new tiers last year, but you still need to answer new questions covering things like in‑app controls, medical or wellness content, and violent themes. If you don’t, your iOS updates get blocked. For a shipping checklist and examples, see our iOS guide complete the new age rating by Jan 31.
What about state laws like Texas’ app store age verification? A federal judge blocked that law from taking effect on December 23, 2025. Keep your work‑in‑progress branches for parental consent APIs and age‑range handling, but don’t hinge January releases on mandates that aren’t in force.
The Monetization Math framework
Here’s a lightweight spreadsheet you can implement in an hour to decide whether to ship external links for a given SKU:
Inputs per SKU: AOV (or ARPPU), subscription or one‑time, monthly web conversion rate from in‑app clicks, processor fee, churn (if subscription), expected fraction of purchases within six months of a Play install, expected fraction of users who click and install an external app within the attribution window.
Costs per SKU: initial acquisition (0% or 3%), ongoing service (10%), external transaction fee when applicable (up to 20% if activated by Google), subscription percentage (10% if activated), fixed install fee ($2.85 apps / $3.65 games directional), processor (2.9%–5% typical).
Outputs: net revenue per conversion, breakeven AOV, and “green light” thresholds by cohort (0–6 months vs. 6+ months from Play install). If Scenario A above turns red, limit external links to subscriptions and customers outside the six‑month window; if Scenario B is green, expand cautiously.

Compliance and privacy checklist
• Information screen: clear, unambiguous, accessible text; no dark patterns or preselected options.
• Token handling: generate external transaction tokens only on intent and record them on the server; verify before fulfillment.
• Parental controls: verify flows with restricted profiles and Family options; avoid inadvertent bypasses.
• Refunds: document a refund SLA and publish it in your receipts and help center.
• Data minimization: don’t hoard PII from web checkouts you don’t need; align with your privacy policy and data retention schedule.
• Incident response: if your web checkout goes down, your app should degrade gracefully and never loop the user between app and web.
Security notes for January releases
Shipping payments means patching: update Android dependencies, and scan your web stack before you expose a new checkout endpoint. If you maintain Android client and backend in Node, mark April 30, 2026 on your calendar—Node.js 20 reaches end of life then. Plan your runtime upgrade while you still have headroom; our Node.js 20 EOL migration playbook shows a 90‑day plan you can run in parallel with your payments work. Also keep an eye on platform security patches; our Android January 2026 security bulletin guide highlights the CVEs worth testing against if you’re touching WebView or deep links.
What to do next
• Decide scope: subscriptions first, one‑time items later. Avoid external app install links unless your model stays green after the per‑install fee.
• Enroll and integrate: External Content Links + Play Billing Library 8.2.1. Wire tokens end‑to‑end.
• Ship the information screen: simple, honest, localized.
• Build the spreadsheet model: simulate 10k/50k/200k monthly conversions, and 0–6 vs. 6+ month cohorts.
• Stage rollout: 10% → 25% → 50% with explicit rollback criteria and observability.
• Close the loop on iOS: finish the App Store age rating update this sprint.
Need deeper dives and templates?
If you want step‑by‑step enrollment screens and API snippets, we’ve published a detailed engineering guide in The Engineering Plan, plus a finance‑friendly explainer in Fees, Flows, ROI. For a one‑pager you can share with stakeholders, see our Builder’s Guide.
Here’s the thing: external links aren’t a silver bullet. They’re a strategic lever that can increase LTV only if you’re ruthless about fee stacking, funnel friction, and the six‑month acquisition window. Ship the integration, keep the knobs server‑side, and iterate with data—not vibes.








Comments
Be the first to comment.